
Specifying actuators 101: Actuator know-how for machine design engineers, Part 1
Learn key tips to simply actuator selection, starting with the initial decision of whether to specify an electric rod actuator or a rodless electromechanical actuator. It's all covered in our eBook, a ready-reference for your next maachine design project.

Motion control keeps material handling systems moving
In these stay-at-home days, online shoppers increase the need for accurate, fast and efficient material handling systems, from processing paper products to packaging, conveying and shipping. Electric actuation is bringing many benefits to applications that have typically been pneumatic.

Linear actuators for gantry and multi-axis systems
Gantry and multi-axis systems are used throughout manufacturing to lift, position and move loads. Actuators and components are used to build two-dimensional designs with a simple XY axis, or three-dimensional designs with XYZ axis.

Roller screw technology for electric actuators
The unique design of a roller screw actuator offers longer life and higher thrust in a smaller package compared to ball screw actuators, increasing a machine designer’s ability to create compact machine concepts.

How electric actuators keep tire manufacturing up to speed
Motion control systems throughout the tire-manufacturing process meet specific requirements for increased quality, faster assembly, improved reliability or flexibility to adjust sizes and changeovers. Many systems are currently driven by pneumatic or hydraulic motion control systems. Manufacturers are increasingly opting for electric systems that are cleaner, faster and more efficient.

Making the case: Why convert a tube-bending machine from hydraulic to electric
Tube-bending machines have been driven by hydraulics for the past 80 years. Operators know how to get the best out of their machines, so why switch to electric cylinders? Yes, there are some disadvantages to going electric, but the fundamental reason to consider making the switch is simple: Electric cylinders make better parts. And that saves money. We'll discuss reasons to consider making the switch and take a look at two examples using electric-weld tubing and fluid-transfer tubing.
Demystifying electronic camming
Electronic cams may at first appear challenging, but electric actuators and motion controllers make them surprisingly easy to configure. Here’s how to approach electronic camming with confidence.

Cheese-making: Automating an ancient art for safety and efficiency
Electric linear motion enhances cheese processing and production.

Linear motion for meat processing
Linear actuators used in meat processing are designed for corrosion resistance, washdown protection and bacterial growth prevention.
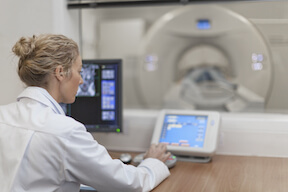
Motion control solutions for medical device applications
Solutions for medical procedures include equipment for radiation treatment, a contrast dye injection, and a specialty machine that safely performs scans on large animals.

 Ask an Engineer
Ask an Engineer